19 Degrees F To C
zacarellano
Sep 19, 2025 · 5 min read
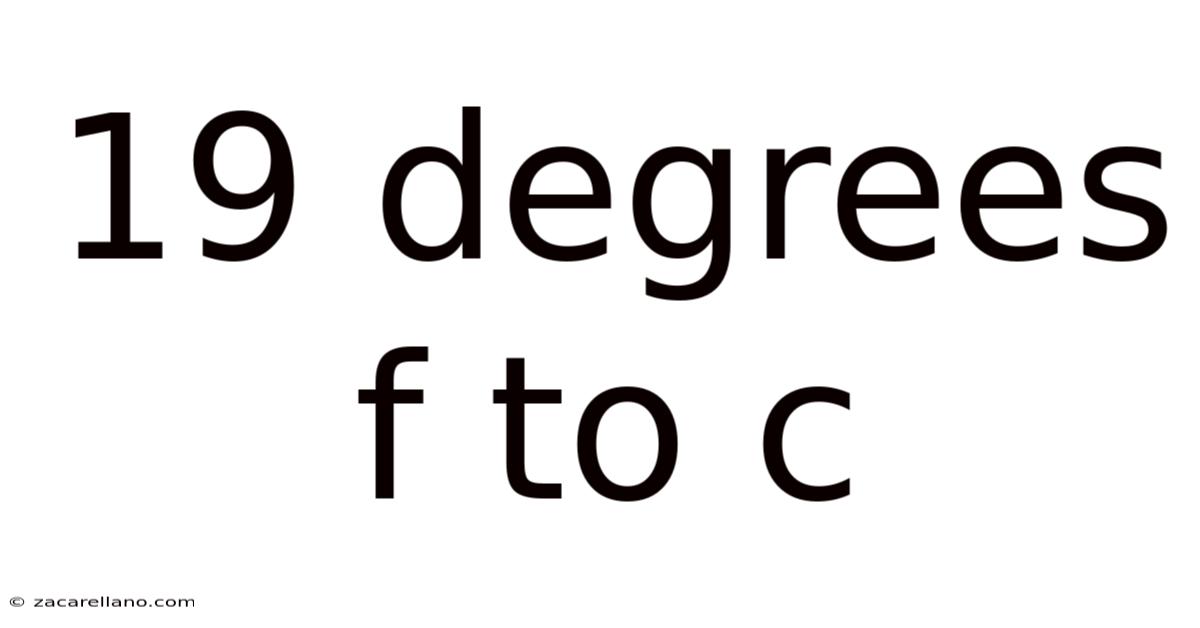
Table of Contents
Converting 19 Degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you curious about how to convert 19 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C)? This seemingly simple conversion is a fundamental concept in understanding temperature scales and is crucial in various fields, from cooking and meteorology to engineering and science. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to perform the calculation but will also delve into the history of these temperature scales, explore the underlying principles, and answer frequently asked questions. We'll also examine practical applications and consider the implications of this specific temperature conversion.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius
Before jumping into the conversion, let's briefly understand the two temperature scales involved: Fahrenheit and Celsius.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): This scale, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, is based on three reference points: the freezing point of a brine solution (0°F), the freezing point of water (32°F), and the average human body temperature (around 96°F). It's predominantly used in the United States and a few other countries.
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius was developed by Anders Celsius in the 18th century. It uses the freezing point of water (0°C) and the boiling point of water (100°C) at standard atmospheric pressure as its defining points. It's the most widely used temperature scale globally and is the preferred scale in scientific contexts.
The Conversion Formula: From Fahrenheit to Celsius
The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
This formula essentially scales and shifts the Fahrenheit reading to align with the Celsius scale. Subtracting 32 accounts for the difference in the freezing point of water between the two scales (32°F vs 0°C), while multiplying by 5/9 adjusts for the different scales' sizes.
Calculating 19 Degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius
Now, let's apply the formula to convert 19°F to °C:
°C = (19°F - 32) × 5/9
°C = (-13) × 5/9
°C = -65/9
°C ≈ -7.22°C
Therefore, 19 degrees Fahrenheit is approximately equal to -7.22 degrees Celsius.
Practical Applications and Significance of -7.22°C
A temperature of -7.22°C is considered quite cold. Here are some real-world implications:
-
Weather: This temperature is typical of a cold winter day in many parts of the world. In some regions, this could lead to freezing conditions, impacting transportation, infrastructure, and even human health.
-
Water: At this temperature, water would be in a solid state (ice) if it's pure water and still.
-
Biology: Many biological processes are significantly affected by temperatures below 0°C. For instance, many plants would suffer damage at this temperature, and several organisms might experience difficulty surviving.
-
Engineering: Engineers consider this temperature range when designing infrastructure and equipment that need to function in cold climates. Materials' properties change significantly at these lower temperatures, necessitating design considerations to mitigate potential problems like cracking or brittleness.
Delving Deeper: Understanding the Linear Relationship
The conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius is a linear transformation. This means that the relationship between the two scales can be represented by a straight line on a graph. The slope of this line is 5/9, and the y-intercept is -32 × 5/9 = -17.78. This linear relationship implies a constant ratio between changes in temperature expressed in Fahrenheit and Celsius. For instance, a 9°F increase is always equal to a 5°C increase. This consistency makes the conversion straightforward and predictable.
Historical Context: The Development of Temperature Scales
The invention of reliable temperature scales was a significant step forward in scientific progress. Understanding the evolution of these scales provides valuable context to appreciating the conversion process. Fahrenheit's scale, while initially based on somewhat arbitrary reference points, has seen refinements over time. Celsius, with its clear and easily reproducible reference points (the freezing and boiling points of water), has gained widespread acceptance due to its simplicity and scientific rigor. The adoption of the Kelvin scale, an absolute temperature scale, further solidified the importance of precise temperature measurement in various scientific disciplines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Why is the conversion formula not simply a ratio? The formula is not just a simple ratio because the zero points of the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales are different. The subtraction of 32 accounts for this offset before applying the scaling factor.
-
Can I convert Celsius to Fahrenheit? Yes, the reverse conversion is equally straightforward. The formula is: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
-
What is the significance of the 5/9 factor? The 5/9 factor represents the ratio of the size of one degree Celsius to one degree Fahrenheit. The Celsius scale is larger than the Fahrenheit scale.
-
Are there other temperature scales? Yes, the Kelvin scale is a crucial scale used in scientific contexts, especially in thermodynamics and physics. It is an absolute temperature scale where 0 Kelvin represents absolute zero, the theoretically lowest possible temperature.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Converting 19 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius (-7.22°C) might seem trivial at first glance, but understanding the process unveils fundamental principles in temperature measurement and the importance of consistent scientific methodology. This seemingly basic conversion demonstrates the linear relationship between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales, highlights the importance of accurate measurements, and illustrates the practical applications of temperature conversions in various fields. By grasping the underlying principles and the historical context, we can appreciate the value of converting between temperature scales not just as a mathematical exercise but as a crucial aspect of understanding our physical world. The ability to accurately convert temperatures allows us to communicate effectively across different contexts and enables accurate analysis and interpretation of data in diverse scientific, engineering, and everyday applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Key Features Of A Graph
Sep 19, 2025
-
St John The Baptist Leonardo
Sep 19, 2025
-
What Is A Scale Copy
Sep 19, 2025
-
Derivative Of A Power Series
Sep 19, 2025
-
Gcf Of 14 And 18
Sep 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 19 Degrees F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.