Fecl3 + Cocl2 Ionic Equation
zacarellano
Sep 23, 2025 · 7 min read
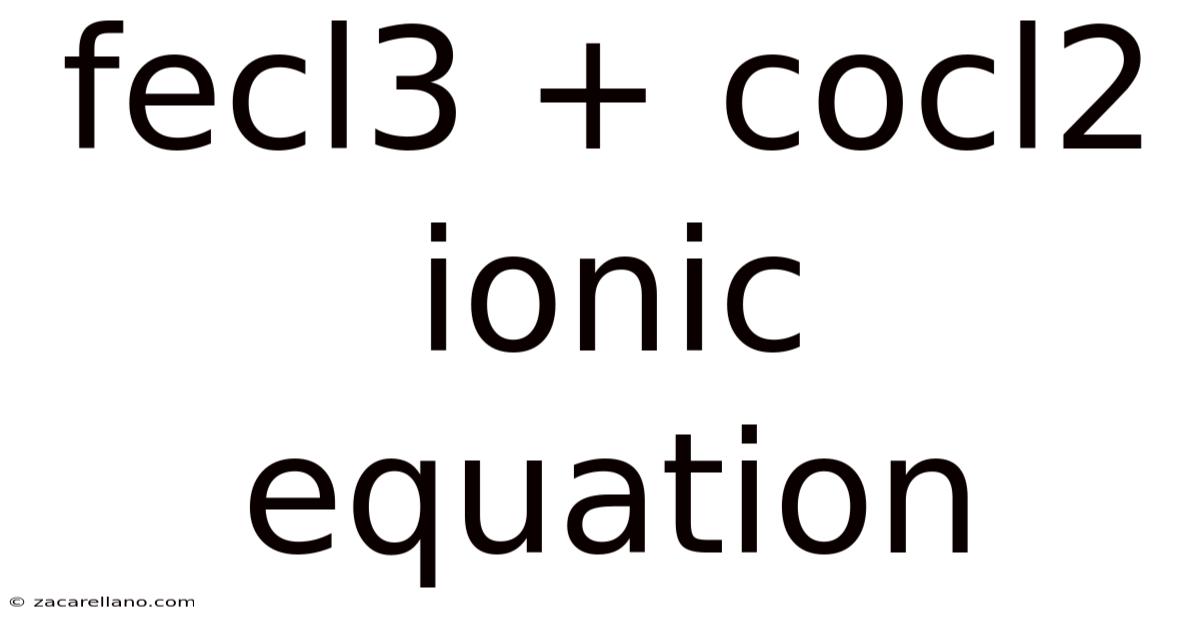
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Reaction: FeCl3 + CoCl2 – An In-Depth Exploration of Ionic Equations
Understanding chemical reactions is fundamental to chemistry. This article delves into the reaction between ferric chloride (FeCl3) and cobalt(II) chloride (CoCl2), exploring its ionic equation, the underlying principles, and potential applications. We'll break down the complexities, making it accessible to both beginners and those seeking a deeper understanding. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to predict and analyze similar reactions involving transition metal salts.
Introduction: Understanding Ionic Compounds and Reactions
Before diving into the specifics of FeCl3 and CoCl2, let's establish a foundational understanding of ionic compounds and reactions. Ionic compounds are formed through the electrostatic attraction between positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). These ions are created when atoms lose or gain electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
FeCl3, or ferric chloride, is an ionic compound consisting of ferric ions (Fe³⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻). Similarly, CoCl2, or cobalt(II) chloride, comprises cobalt(II) ions (Co²⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻). When these two ionic compounds are mixed in an aqueous solution, they dissociate into their respective ions. This dissociation is crucial to understanding the reaction.
The Ionic Equation: Deconstructing the Reaction
The reaction between FeCl3 and CoCl2 in aqueous solution doesn't involve a typical double displacement reaction leading to the formation of a precipitate. Instead, the reaction is primarily driven by the interaction of the metal ions and the solvent. There's no significant chemical change in the composition of the ions themselves. The "reaction" is more accurately described as a redistribution of ions in the solution.
Let's write the complete ionic equation to represent what happens when FeCl3 and CoCl2 are mixed in water:
Fe³⁺(aq) + 3Cl⁻(aq) + Co²⁺(aq) + 2Cl⁻(aq) → Fe³⁺(aq) + Co²⁺(aq) + 5Cl⁻(aq)
Explanation:
- (aq) denotes that the ions are in aqueous solution (dissolved in water).
- The equation shows the dissociation of FeCl3 into Fe³⁺ and 3Cl⁻ ions and CoCl2 into Co²⁺ and 2Cl⁻ ions.
- No new compounds are formed; the ions simply remain in solution. The chloride ions are spectator ions, meaning they don't participate in any significant chemical change.
The Net Ionic Equation:
Since the chloride ions are spectator ions, they can be cancelled out from both sides of the complete ionic equation. This leaves us with the net ionic equation:
Fe³⁺(aq) + Co²⁺(aq) → No Reaction
This net ionic equation highlights the crucial point: there's no net chemical reaction between FeCl3 and CoCl2 in aqueous solution. The ions simply coexist in the solution.
Factors Influencing Ion Behavior in Solution
Several factors influence the behavior of ions in solution:
- Solubility: The solubility of ionic compounds determines their ability to dissociate into ions in water. Both FeCl3 and CoCl2 are highly soluble in water, ensuring complete dissociation.
- Concentration: The concentration of ions in the solution affects the interactions between them. Higher concentrations can potentially lead to increased interaction but, in this case, do not result in a new chemical compound.
- Temperature: Temperature affects the solubility of ionic compounds and the kinetic energy of the ions, indirectly influencing their interactions.
- pH: The pH of the solution can affect the speciation of metal ions, particularly transition metals like iron and cobalt, potentially influencing their behavior. However, in a neutral or slightly acidic solution, this effect might not be pronounced for this specific reaction.
Exploring the Properties of FeCl3 and CoCl2
To fully appreciate the lack of reaction, let's examine the individual properties of FeCl3 and CoCl2:
Ferric Chloride (FeCl3):
- Appearance: Brownish-black solid. Aqueous solutions appear yellow-brown due to the complex formation of hydrated iron(III) ions.
- Uses: Water treatment, etching, and as a catalyst in various chemical reactions.
- Reactions: FeCl3 participates in numerous reactions, including redox reactions and complex formation with ligands.
Cobalt(II) Chloride (CoCl2):
- Appearance: Blue solid. Aqueous solutions are typically pink, but the color can change depending on concentration and temperature due to the formation of different hydrated cobalt(II) complexes. This color change is a well-known example of a coordination compound's sensitivity to environment.
- Uses: Electroplating, as a catalyst, and in the production of pigments.
- Reactions: CoCl2 also participates in various reactions, including complex formation, redox reactions, and precipitation reactions with some anions.
Why No Reaction Occurs: A Deeper Dive
The absence of a reaction between FeCl3 and CoCl2 in aqueous solution can be explained by several factors:
-
No Precipitate Formation: No insoluble compound forms that would drive a precipitation reaction. Both chlorides are highly soluble, and neither iron(III) nor cobalt(II) forms an insoluble chloride.
-
No Weak Acid/Base Reaction: There's no significant acid-base reaction between the ions. While hydrated metal ions can exhibit some acidic or basic properties, this reaction doesn't involve a strong enough acid-base interaction to form a new product.
-
No Redox Reaction: There's no apparent redox reaction. While both iron and cobalt can exist in multiple oxidation states, the conditions are not conducive for an electron transfer between Fe³⁺ and Co²⁺. A redox reaction would require a change in the oxidation state of at least one of the metal ions.
-
Complex Formation (Limited): While both iron and cobalt are known to form complexes with ligands, the chloride ion is a relatively weak ligand. The formation of complexes involving chloride is not energetically favorable enough to significantly change the composition of the solution. The dominant species remain the hydrated metal ions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What happens if I mix FeCl3 and CoCl2 in a non-aqueous solvent?
A1: The behavior of FeCl3 and CoCl2 in a non-aqueous solvent will differ significantly. The absence of water prevents the dissociation of the ionic compounds into their constituent ions. The outcome will depend heavily on the specific solvent used and its interaction with the metal chlorides. New complexes or other interactions might occur depending on the solvent's properties.
Q2: Could a reaction occur if I added another reagent?
A2: Yes, adding another reagent could potentially induce a reaction. For instance, adding a ligand that forms stable complexes with either Fe³⁺ or Co²⁺ could lead to a change in the solution's properties. Similarly, the addition of a strong reducing or oxidizing agent could induce a redox reaction.
Q3: Is it safe to handle FeCl3 and CoCl2?
A3: Both FeCl3 and CoCl2 are corrosive and should be handled with appropriate safety precautions. Always wear gloves, eye protection, and a lab coat when handling these chemicals. Ensure adequate ventilation and follow proper disposal procedures.
Q4: What are some practical applications of this knowledge?
A4: Understanding the behavior of ionic compounds in solution is critical in various applications, including:
- Analytical chemistry: Predicting the behavior of ions in solution is crucial for developing analytical techniques.
- Material science: Controlling the interactions between metal ions is essential in synthesizing new materials.
- Environmental science: Understanding the fate and transport of metal ions in the environment is crucial for environmental remediation.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Understanding
The reaction, or rather, the lack of a significant reaction, between FeCl3 and CoCl2 in aqueous solution demonstrates the importance of understanding the factors influencing ionic interactions. While there is no net chemical change in the formation of a new compound, the ions simply coexist in the solution. This seemingly simple reaction serves as a powerful example of the complexities of ionic interactions and highlights the importance of considering solubility, concentration, and the inherent properties of individual ions when predicting the outcome of chemical reactions. The principles discussed here are applicable to a wider range of ionic compounds and lay the groundwork for a deeper appreciation of solution chemistry. Further exploration of complex formation, redox reactions, and non-aqueous solvents will enrich your understanding of these fascinating interactions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Sat Boot Camp Near Me
Sep 23, 2025
-
Converting Kilograms To Grams Worksheet
Sep 23, 2025
-
Did Tyrannosaurus Rex Lay Eggs
Sep 23, 2025
-
Lcm Of 9 And 16
Sep 23, 2025
-
Is Appears A Linking Verb
Sep 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Fecl3 + Cocl2 Ionic Equation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.